Process Control - GATE-CH Questions
Home -> GATE Questions with Solutions at MSubbu.Academy -> Process Control ->
Advanced Control
GATE-CH-2003-79-ctrl-2mark
In the case of a feed-forward control scheme, which of the following is NOT true?
It is insensitive to modeling errors
Cannot cope with unmeasured disturbances
It waits until the effect of the disturbance has been felt by the system before control action is taken
Requires good knowledge of the process model
Requires identification of all possible disturbances and their direct measurement
GATE-CH-2005-11-ctrl-1mark
Cascade control comes under the control configuration which uses
GATE-CH-2007-62-ctrl-2mark
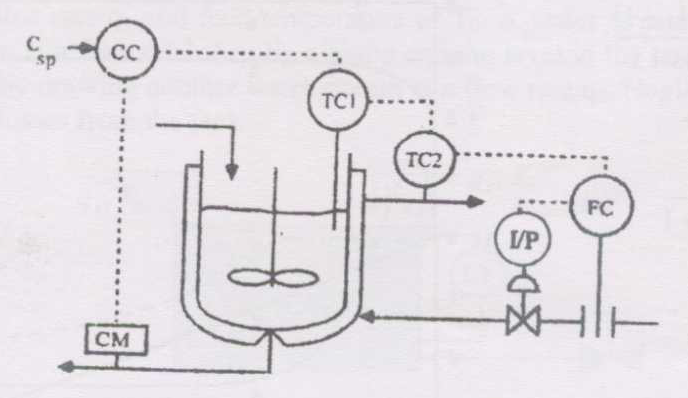
Consider the following instrumentation diagram for a chemical reactor. \(C_{SP}\) represents a concentration setpoint.
Match the items in column A with the corresponding items given in column B.
Column A
Column B
P) control strategy
1) feed forward control
Q) primary control variable
2) cascade control
R) slowest controller
3) concentration in the reactor
S) fastest controller
4) reactor temperature
5) jacket temperature
6) concentration controller
7) reactor temperature controller
8) jacket temperature controller
9) flow controller
10) selective control
GATE-CH-2004-81-ctrl-2mark
The process and disturbance transfer functions for a system are given by
\( \begin{align*} G_p(s) &= \frac{\bar{y}(s)}{m(s)} = \frac{2}{(2s+1)(5s+1)} \\ G_d(s) &= \frac{\bar{y}(s)}{d(s)} = \frac{1}{(2s+1)(5s+1)} \end{align*} \)
The feed forward controller transfer function that will keep the process output constant for changes in disturbance is
GATE-CH-2014-46-ctrl-2mark
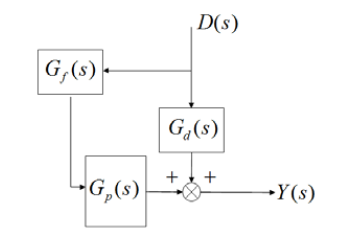
Given below is a simplified block diagram of a feedforward control system.
The transfer function of the process is \(G_p(s)=\dfrac{5}{s+1}\) and the disturbance transfer function is \(G_d(s)=\dfrac{1}{s^2+2s+1}\) . The transfer function of the PERFECT feedforward controller, \(G_f(s)\) is
GATE-CH-2008-65-ctrl-2mark-DIFFER
Match the following:
GROUP 1
GROUP 2
(P) Ziegler Nichols
(1) Process reaction curve
(Q) Under damped response
(2) Decay ratio
(R) Feed-forward control
(3) Frequency response
(4) Disturbance measurement
[Index ]
Last Modified on: 02-May-2024
Chemical Engineering Learning Resources - msubbuwww.msubbu.in